Complex Components
Learn how to use BELLATRIX complex web components.
Introduction
The difference between a table and grid is that usually, the grids are more complex than a regular HTML table. In them, you can have dynamic data. Moreover, inside the column, you can have other HTML elements such as buttons, text fields, selects, other tables. Or you can filter, sort the columns, and have paging for the grid. Instead of getting specific cells or rows by custom locators- we have created the Table and Grid controls, which ease the selection of cells/rows and assertion of the data. Moreover, in many cases there isn’t a unique item which you can use to select the row/cell.
Tables

Example
@ExecutionBrowser(browser = Browser.CHROME, lifecycle = Lifecycle.REUSE_IF_STARTED)
public class TableTests extends WebTest {
private List<User> expectedUsers;
private Table table() {
return app().create().byId(Table.class, "table1")
.setColumn("Last Name")
.setColumn("First Name")
.setColumn("Email")
.setColumn("Due")
////.setColumn("Web Site") // this column won't be asserted if you use the assertTable method.
.setColumn("Action");
}
@BeforeEach
public void testInit() {
app().navigate().toLocalPage("testpages/table/table.html");
expectedUsers = new ArrayList<>();
expectedUsers.add(new User("John", "Smith", "jsmith@gmail.com", "http://www.jsmith.com", "$50.00"));
expectedUsers.add(new User("Frank", "Bach", "fbach@yahoo.com", "http://www.frank.com", "$51.00"));
expectedUsers.add(new User("Jason", "Doe", "jdoe@hotmail.com", "http://www.jdoe.com", "$100.00"));
expectedUsers.add(new User("Tim", "Conway", "tconway@earthlink.net", "http://www.timconway.com", "$50.00"));
}
@Test
public void assertMiscData() {
Assertions.assertEquals(expectedUsers.get(0).getEmail(), table().getItems(User.class).get(0).getEmail());
table().assertTable(expectedUsers);
Assertions.assertEquals("Action", table().getHeaderNames().get(table().getHeaderNames().size() - 1));
}
@Test
public void assertCells() {
table().forEachCell(cell -> Assertions.assertEquals("14px", cell.getCssValue("font-size")));
table().getCell("First Name", 1).validateTextIs("Frank");
table().getCell(1, 2).validateTextIs("Jason");
table().getCell(User.class, cell -> cell.getEmail(), 1).validateTextIs("fbach@yahoo.com");
var cells = table().getCells(cell -> cell.getText().toLowerCase().startsWith("j"));
Assertions.assertEquals(4, cells.size());
var matchingCell = table().getFirstOrDefaultCell(cell -> cell.getText().toLowerCase().startsWith("j"));
matchingCell.validateTextIs("John");
}
@Test
public void assertSpecificRow() {
var firstRow = table().getRow(0);
Assertions.assertEquals(0, firstRow.getIndex());
Assertions.assertTrue(firstRow.getHtml().contains("</td>"));
firstRow.validateHtmlContains("</td>");
var firstCell = table().getRow(0).getCell(0);
firstCell.validateTextIs("Smith");
var secondCell = firstRow.getCell("Email");
secondCell.validateTextIs("jsmith@gmail.com");
var cells = firstRow.getCells();
Assertions.assertEquals(6, cells.size());
var matchingCells = firstRow.getCells(cell -> cell.getText().toLowerCase().contains("smith"));
Assertions.assertEquals(3, matchingCells.size());
var matchingCell = firstRow.getFirstOrDefault(cell -> cell.getText().toLowerCase().contains("smith"));
matchingCell.validateTextIs("Smith");
Assertions.assertEquals("jsmith@gmail.com", firstRow.getItem(User.class).getEmail());
firstRow.assertRow(expectedUsers.get(0));
}
@Test
public void assertSpecificCell() {
var firstCell = table().getCell(0, 0);
Assertions.assertEquals(0, firstCell.getRow());
Assertions.assertEquals(0, firstCell.getColumn());
Assertions.assertEquals("Smith", firstCell.getText());
firstCell.validateTextIs("Smith");
var thirdCell = table().getCell(0, 2);
Assertions.assertEquals("Doe", thirdCell.getText());
thirdCell.validateTextIs("Doe");
}
@Test
public void assertColumns() {
var secondColumn = table().getColumn(1);
Assertions.assertEquals("John", secondColumn.get(0).getText());
secondColumn.get(0).validateTextIs("John");
secondColumn = table().getColumn("First Name");
Assertions.assertEquals("John", secondColumn.get(0).getText());
secondColumn.get(0).validateTextIs("John");
}
}
Explanations
private Table table() {
return app().create().byId(Table.class, "table1")
.setColumn("Last Name")
.setColumn("First Name")
.setColumn("Email")
.setColumn("Due")
////.setColumn("Web Site") // this column won't be asserted if you use the assertTable method.
.setColumn("Action");
}
BELLATRIX gives you API for easing the work with HTML tables. Through the setColumn you map the headers of the table if for some reason you don’t want some column, just don’t add it. The method returns a list of all rows’ data as Java data mapped to the map you provided. Since we haven’t the setColumn for the WebSite- this property won’t be asserted if you use the assertTable method.
General Methods
Assertions.assertEquals(expectedUsers.get(0).getEmail(), table().getItems(User.class).get(0).getEmail());
You can get all rows as instances of a specific class through the getItems method.
table().assertTable(expectedUsers);
Compares all table rows to the expected entities. Each row is internally converted to the type of the expected entities.
Assertions.assertEquals("Action", table().getHeaderNames().get(table().getHeaderNames().size() - 1));
Cells’ Related Methods
You can get all header names. Doubled headers are returned as one entry and separated by space.
table().forEachCell(cell -> Assertions.assertEquals("14px", cell.getCssValue("font-size")));
As a shortcut, you can iterate over all table cells through the forEachCell method.
table().getCell("First Name", 1).validateTextIs("Frank");
You can get a particular cell as BELLATRIX element mentioning the column header and row number.
table().getCell(1, 2).validateTextIs("Jason");
You can get a particular cell as BELLATRIX element mentioning the row and column number.
table().getCell(User.class, cell -> cell.getEmail(), 1).validateTextIs("fbach@yahoo.com");
You can get a particular cell by header expression and row number.
var cells = table().getCells(cell -> cell.getText().toLowerCase().startsWith("j"));
Assertions.assertEquals(4, cells.size());
You can get particular cells by a selector.
var matchingCell = table().getFirstOrDefaultCell(cell -> cell.getText().toLowerCase().startsWith("j"));
matchingCell.validateTextIs("John");
As a shortcut, you can get the first cell matching a given condition through the getFirstOrDefaultCell method.
Assertions.assertEquals(0, firstCell.getRow());
Assertions.assertEquals(0, firstCell.getColumn());
You can get the cell row and column.
Assertions.assertEquals("Smith", firstCell.getText());
You can get the cell’s text.
firstCell.validateTextIs("Smith");
You can use built-in BELLATRIX ensure methods to assert the cell attributes.
var thirdCell = table().getCell(0, 2);
Assertions.assertEquals("Doe", thirdCell.getText());
You can get the cell by row and column index.
Rows’ Related Methods
var firstRow = table().getRow(0);
You can get a specific row using the getRow method by the index of the row.
Assertions.assertEquals(0, firstRow.getIndex());
You can get the index of a given row through the getIndex method.
Assertions.assertTrue(firstRow.getHtml().contains("</td>"));
You can get the HTML through the getHtml method.
firstRow.validateHtmlContains("</td>");
If you only need to assert the inner HTML you can use the built-in BELLATRIX ensure methods.
var firstCell = table().getRow(0).getCell(0);
There are many ways to get a specific cell through the indexer and the getCell methods.
var secondCell = firstRow.getCell("Email");
secondCell.validateTextIs("jsmith@gmail.com");
You can get a cell by header name.
var cells = firstRow.getCells();
Assertions.assertEquals(6, cells.size());
You can get all row cells through the getCells method.
var matchingCells = firstRow.getCells(cell -> cell.getText().toLowerCase().contains("smith"));
Assertions.assertEquals(3, matchingCells.size());
You can get the cells matching a condition.
var matchingCell = firstRow.getFirstOrDefault(cell -> cell.getText().toLowerCase().contains("smith"));
matchingCell.validateTextIs("Smith");
You can get the first cell matching a condition through the getFirstOrDefaultCell method.
Assertions.assertEquals("jsmith@gmail.com", firstRow.getItem(User.class).getEmail());
You can convert a row to an instance of a specific class through the getItem method.
firstRow.assertRow(expectedUsers.get(0));
You can compare a row to an instance of a specific class. The row is internally converted to the type of the expected object.
Columns’ Related Methods
var secondColumn = table().getColumn(1);
Assertions.assertEquals("John", secondColumn.get(0).getText());
You can get the cells of a particular column mentioning the column number.
secondColumn.get(0).validateTextIs("John");
You can use built-in BELLATRIX ensure methods to assert the cell attributes.
secondColumn = table().getColumn("First Name");
Assertions.assertEquals("John", secondColumn.get(0).getText());
You can get the cells of a particular column mentioning the column name.
Data Objects
public class User {
@TableHeader(name = "Last Name")
private String lastName;
@TableHeader(name = "First Name")
private String firstName;
@TableHeader(name = "Email")
private String email;
@TableHeader(name = "Due")
private String due;
@TableHeader(name = "Web Site")
private String website;
// getters and setters
}
In order getItems to be able to work you need to map the properties to headers through the TableHeader attribute this is how we handle differences between the property name, spaces in the headers and such.
Grids
The difference between a table and grid is that usually, the grids are more complex than a regular HTML table. In them, you can have dynamic data. Moreover, inside the column, you can have other HTML elements such as buttons, text fields, selects, other tables. Or you can filter, sort the columns, and have paging for the grid. Instead of getting specific cells or rows by custom locators-we have created the Table and Grid controls, which ease the selection of cells/rows and assertion of the data. Moreover, in many cases there isn’t a unique item which you can use to select the row/cell.
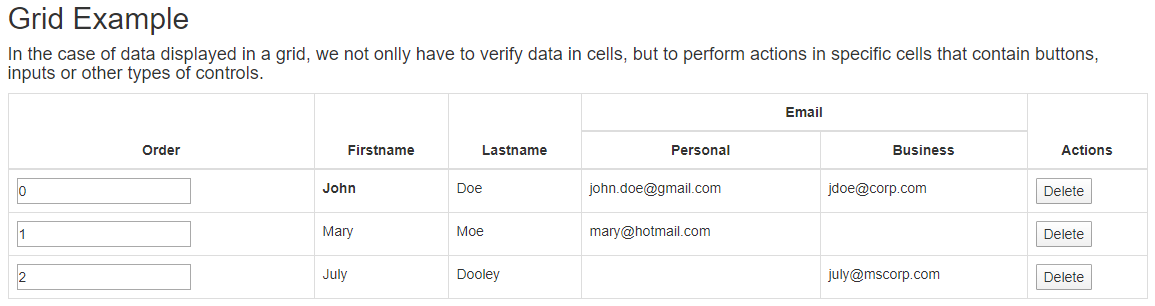
Example
@ExecutionBrowser(browser = Browser.CHROME, lifecycle = Lifecycle.REUSE_IF_STARTED)
public class GridTests extends WebTest {
private List<Employee> expectedItems;
private Grid grid() {
return app().create().byId(Grid.class, "sampleGrid")
.setColumn("Order", TextInput.class, new TagFindStrategy("input"))
.setColumn("Firstname")
.setColumn("Lastname")
.setColumn("Email Personal")
.setColumn("Email Business")
.setColumn("Actions", Button.class, new XPathFindStrategy("./input[@type='button']"));
}
@BeforeEach
public void testInit() {
app().navigate().toLocalPage("testpages/grid/grid.html");
List<Employee> expectedItems = new ArrayList<>();
expectedItems.add(new Employee("0", "John", "Doe", "john.doe@gmail.com", "jdoe@corp.com"));
expectedItems.add(new Employee("1", "Mary", "Moe", "mary@hotmail.com", ""));
expectedItems.add(new Employee("2", "July", "Dooley", "", "july@mscorp.com"));
}
@Test
public void assertGridCells() {
grid().forEachCell(cell -> Assertions.assertEquals("14px", cell.getCssValue("font-size")));
grid().getCell("Firstname", 1).validateTextIs("Mary");
grid().getCell(0, 1).validateTextIs("John");
grid().getCell(Employee.class, cell -> cell.getPersonalEmail(), 1).validateTextIs("mary@hotmail.com");
var matchingCells = grid().getCells(TableCell.class, cell -> cell.getText().startsWith("J"));
Assertions.assertEquals(2, matchingCells.size());
grid().getCell("Email Business", 0).validateTextIs("jdoe@corp.com");
var firstRowEmail = grid().getRow(0).getCell("Email Personal");
grid().getCell("Action", 0).as(Button.class).click();
var firstRowEmailAfterDelete = grid().getRow(0).getCell("Email Personal");
Assertions.assertNotEquals(firstRowEmail, firstRowEmailAfterDelete);
}
@Test
public void assertObjectsData() {
var expectedObj = expectedItems.get(0);
var actualObj = grid().getItems(Employee.class).get(0);
EntitiesAsserter.assertAreEqual(expectedObj, actualObj);
grid().getRow(0).assertRow(expectedObj);
grid().assertTable(Employee.class, expectedItems);
Assertions.assertEquals("Email Personal", grid().getHeaderNames().stream().filter(header -> header.startsWith("Email")).findFirst().orElse(null));
}
@Test
public void assertRows() {
Assertions.assertEquals(3, grid().getRows().size());
grid().forEachRow(row -> row.createByXPath(Button.class, ".//input[@type='button']").validateIsVisible());
var secondRow = grid().getRow(1);
Assertions.assertEquals(1, secondRow.getCells(TableCell.class, cell -> Objects.equals(cell.getText(), "Mary")).size();
var firstRow = grid().getRow(0);
firstRow = grid().getRows(TableCell.class, cell -> cell.getText().contains("J")).stream().findFirst().orElse(null);
firstRow = grid().getFirstOrDefaultRow(TableCell.class, cell -> cell.getText().contains("J"));
}
@Test
public void assertSpecificRow() {
var firstRow = grid().getRow(0);
Assertions.assertEquals(0, firstRow.getIndex());
Assertions.assertTrue(firstRow.getHtml().contains("</td>"));
firstRow.validateHtmlContains("</td>");
var firstCell = firstRow.getCell("Order");
firstCell.as(TextInput.class).validateValueIs("0");
var secondCell = firstRow.getCell(1);
secondCell.validateTextIs("John");
var cells = firstRow.getCells();
Assertions.assertEquals(6, cells.size());
var textFields = firstRow.getCells().stream()
.filter(cell -> cell.getText().startsWith("John") || cell.getText().startsWith("john"))
.map(cell -> (TableCell) cell)
.toList();
Assertions.assertEquals(2, textFields.size());
var firstInputCell = firstRow.getFirstOrDefault(TextInput.class, cell -> "input".equals(cell.getTagName()));
firstInputCell.validateValueIs("0");
Employee employee = firstRow.getItem(Employee.class);
Assertions.assertEquals("John Doe", employee.getFirstName() + " " + employee.getLastName());
firstRow.assertRow(expectedItems.get(0));
}
@Test
public void assertSpecificCell() {
var secondCell = grid().getCell(0, 1);
Assertions.assertEquals(0, secondCell.getRow());
Assertions.assertEquals(1, secondCell.getColumn());
Assertions.assertEquals("John", secondCell.getText());
Assertions.assertEquals("<b>John</b>", secondCell.getHtml());
var firstCell = grid().getCell(0, 0);
firstCell.as(TextInput.class).validateValueIs("0");
Assertions.assertEquals("0", firstCell.as(TextInput.class).getValue());
}
@Test
public void assertColumns() {
var firstColumn = grid().getColumn(0);
firstColumn.get(0).as(TextInput.class).validateValueIs("0");
firstColumn = grid().getColumn("Order");
firstColumn.get(0).as(TextInput.class).validateValueIs("0");
Assertions.assertEquals("Email Personal", grid().getGridColumnNameByIndex(3));
}
}
Explanations
private Grid grid() {
return app().create().byId(Grid.class, "sampleGrid")
.setColumn("Order", TextInput.class, new TagFindStrategy("input"))
.setColumn("Firstname")
.setColumn("Lastname")
.setColumn("Email Personal")
.setColumn("Email Business")
.setColumn("Actions", Button.class, new XPathFindStrategy("./input[@type='button']"));
}
BELLATRIX gives you API for easing the work with HTML grids. Through the setColumn you map the headers of the table if for some reason you don’t want some column, just don’t add it. The method returns a list of all rows’ data as Java data mapped to the map you provided. Since we haven’t used the setColumn for the WebSite- this property won’t be asserted if you use the assertTable method. You can get the cell converted to the element specified by the grid setColumn method. Also, since some of this simple controls sometimes are wrapped inside DIV or SPAN elements, you can specify additional locator for finding the element.
General Methods
var expectedObj = expectedItems.get(0);
var actualObj = grid().getItems(Employee.class).get(0);
You can get all rows as instances of a specific class through the getItems method.
grid().getRow(0).assertRow(expectedObj);
Instead of first casting the items and then to get them by index and then assert them manually. You can get specific row through getRow method and use the built-in assertRow method to verify the row’s data.
grid().assertTable(Employee.class, expectedItems);
Compares all grid rows to the expected entities. Each row is internally converted to the type of the expected entities.
Assertions.assertEquals("Email Personal", grid().getHeaderNames().stream().filter(header -> header.startsWith("Email")).findFirst().orElse(null));
You can get all header names. Doubled headers are returned as one entry and separated by space.
Cells’ Related Methods
Assertions.assertEquals(0, secondCell.getRow());
Assertions.assertEquals(1, secondCell.getColumn());
You can get the cell row and column.
Assertions.assertEquals("John", secondCell.getText());
You can get the cell inner text.
Assertions.assertEquals("<b>John</b>", secondCell.getHtml());
You can get the cell inner HTML.
var firstCell = grid().getCell(0, 0);
firstCell.as(TextInput.class).validateValueIs("0");
You can get the cell converted to a specific element and use the element’s specific API.
ssertions.assertEquals("0", firstCell.as(TextInput.class).getValue());
You can get the cell converted to the element specified.
Rows’ Related Methods
Assertions.assertEquals(3, grid().getRows().size());
You can get the grid rows (without the header ones) through the getRows method.
grid().forEachRow(row -> row.createByXPath(Button.class, ".//input[@type='button']").validateIsVisible());
As a shortcut, you can iterate over the grid rows through the forEachRow method.
var secondRow = grid().getRow(1);
Assertions.assertEquals(1, secondRow.getCells(TableCell.class, cell -> Objects.equals(cell.getText(), "Mary")).size());
You can get a specific row by its index through the getRow method.
var firstRow = grid().getRow(0);
firstRow = grid().getRows(TableCell.class, cell -> cell.getText().contains("J")).stream().findFirst().orElse(null);
You can get all rows matching a given condition through the getRows method.
firstRow = grid().getFirstOrDefaultRow(TableCell.class, cell -> cell.getText().contains("J"));
As a shortcut, you can get the first row matching a given condition through the getFirstOrDefaultRow method.
Assertions.assertEquals(0, firstRow.getIndex());
You can get the index of a given row through the getIndex method.
Assertions.assertTrue(firstRow.getHtml().contains("</td>"));
firstRow.validateHtmlContains("</td>");
You can get the HTML through the getHtml method.
var firstCell = firstRow.getCell("Order");
firstCell.as(TextInput.class).validateValueIs("0");
There are many ways to get a specific cell through the indexer and the getCell methods.
var cells = firstRow.getCells();
Assertions.assertEquals(6, cells.size());
You can get all row cells through the getCells method.
var textFields = firstRow.getCells().stream()
.filter(cell -> cell.getText().startsWith("John") || cell.getText().startsWith("john"))
.map(cell -> (TableCell) cell)
.toList();
Assertions.assertEquals(2, textFields.size());
You can get the cells matching a condition. Also, they will be returned as elements of a type of your choice.
var firstInputCell = firstRow.getFirstOrDefault(TextInput.class, cell -> "input".equals(cell.getTagName()));
firstInputCell.validateValueIs("0");
You can get the first cell matching a condition through the getFirstOrDefaultCell method.
Assertions.assertEquals("John Doe", employee.getFirstName() + " " + employee.getLastName());
You can convert a row to an instance of a specific class through the getItem method.
firstRow.assertRow(expectedItems.get(0));
You can compare a row to an instance of a specific class. The row is internally converted to the type of the expected object.
Columns’ Related Methods
var firstColumn = grid().getColumn(0);
firstColumn.get(0).as(TextInput.class).validateValueIs("0");
You can get the cells of a particular column mentioning the column number.
firstColumn = grid().getColumn("Order");
firstColumn.get(0).as(TextInput.class).validateValueIs("0");
You can get the cells of a particular column mentioning the column name.
Assertions.assertEquals("Email Personal", grid().getGridColumnNameByIndex(3));
You can get the name of a column mentioning its index.
Data Objects
public class Employee {
@TableHeader(name = "Order")
private String order;
@TableHeader(name = "Firstname")
private String firstName;
@TableHeader(name = "Lastname")
private String lastName;
@TableHeader(name = "Email Business")
private String businessEmail;
@TableHeader(name = "Email Personal")
private String personalEmail;
// getters and setters
}
In order getItems to be able to work you need to map the properties to headers through the TableHeader attribute this is how we handle differences between the property name, spaces in the headers and such.